 G. Moradi, A. R. Eslami, S. Firouzi
G. Moradi, A. R. Eslami, S. Firouzi
Key words: Consolidation, farm, agriculture, social, economic, socioeconomic.
Abstract
One of the important issues that come up in recent decades has been the fragmentation of agricultural land and frequency of plots. Fragmentation of plots and being small is one of the challenges and major obstacles in the way of increasing production and ultimately the development of agriculture. In recent years, agricultural production has not been commensurate with the growth of population. Continue reading Socio-economical effects of land consolidation in North of Iran (Case study: farms of Masal County)
Month: May 2015
Effect of organic fertilizers on apparent nitrogen utilization and yield of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) as influenced by fertilizer timing
Paul Kinoti Ng’ang’a, Katrin Meriel Jezik
Key words: Organic nitrogen fertilizers, apparent N utilization, N mineralization, yield, sweet pepper.
Abstract
A glasshouse experiment was carried out at the University of Natural resources and Life Sciences, Vienna, Austria during the months of April to September in both 2012 and 2013 to investigate the effect of organic fertilizers on apparent nitrogen utilization and yield of sweet pepper as influenced by fertilizer timing. Continue reading Effect of organic fertilizers on apparent nitrogen utilization and yield of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) as influenced by fertilizer timing
Genetic diversity among different Crataegus azarolus L. populations using RAPD markers in Iran
Fariba Sharifnia, Nasim Seyedipour, S. Abodolhamid Angaji, Fahimeh Salimpour, Roya Razavipour
Key words: Crataegus azarolus, phenogram, genotype, Iran, RAPD.
Abstract
The genus Crataegus azarolus L. is well distributed in Iran as a wild plant, with numerous, inherently variable population and genotypes. In flora of Iran this species is divides into tree independent species, while Christensen believed all of them are varieties of C. azarolus. Continue reading Genetic diversity among different Crataegus azarolus L. populations using RAPD markers in Iran
Effect of terminal high temperature imposed by late sowing on phenological traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
 Md. Nur Alam, Md. Abdul Mannaf, Md. Abu Zaman Sarker, Mst Masuma Akhter
Md. Nur Alam, Md. Abdul Mannaf, Md. Abu Zaman Sarker, Mst Masuma Akhter
Key words: Temperature, phenological traits, heat tolerant genotypes.
Abstract
With a views to observe the effect of prevailing air temperature at irrigated late sowing (ILS) conditions on phenological traits of advanced wheat genotypes and to identify heat tolerant genotypes, the trial was carried out in the research field of Wheat Research Centre, Bangladesh Agricultural Research institute (BARI), Nashipur, Dinajpur in the season of 2011-12. The treatments were four dates of sowing viz. 30 Nov (D1), 15 Dec (D2), 30 Dec (D3), 14 Jan (D4) and four genotypes viz. BARI Gom 26 (V1), BAW 1051 (V2), BAW 1120 (V3), BAW 1141(V4) . The genotypes V2, V3, and V4 were taken as tested genotypes and V1 as check. The design was split-plot with three replications. In ILS conditions, the genotypes phased high temperature stress that significantly reduced the duration of booting, heading, anthesis and physiological maturity stages of all genotypes compared as irrigated timely sowing (ILS, D1) condition since those faced 21 to 25.8oC average mean temperature during booting to physiological maturity stages from 19 February to 09 April, 2012 (10 days interval minimum and maximum temperature was averaged). All genotypes sown on 30 Nov. and 15 Dec. produced yield more than 4 t ha-1 but produced less than 4 t ha-1 in other ILS conditions except BAW 1141 seeded on 30 December. Considering overall performance, BAW 1120 and BAW 1141 may be cultivated up to 15 December and 30 December to get yield 3.34 t ha-1 and 4.15 t ha-1, respectively as heat tolerant genotypes.
Read Full Article: Volume 3, Number 3, March 2013 – IJAAR
Publish on: International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR)
Comparative studies of Indian and Malaysian Thapaocleidus siamensis using molecular marker
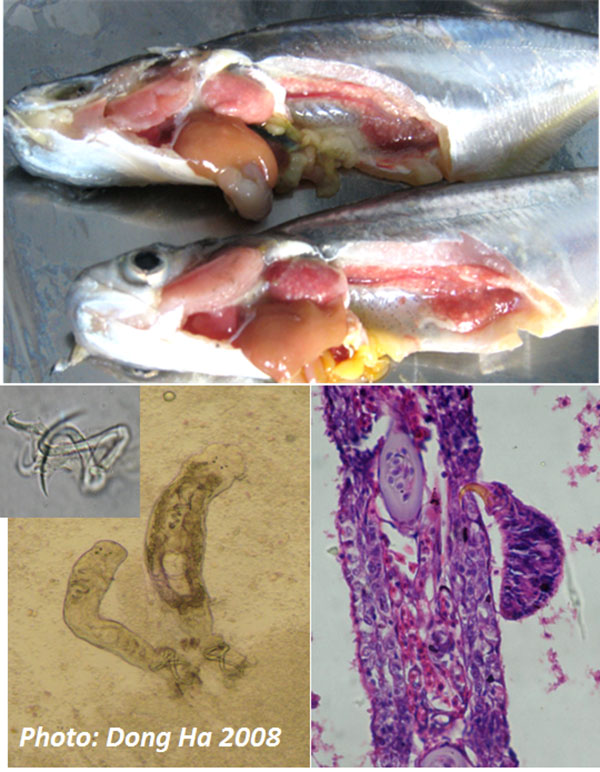 Saroj Rajvanshi, Nirupama Agrawal
Saroj Rajvanshi, Nirupama Agrawal
Key words: Thparocleidus, comparative study, motif identification, secondary structure.
Abstract
In the present communication the sequence of an exotic species of genus Thaparocleidus i.e T. siamensis (Lim, 1990) Lim, 1996 (collected in India) has been compared with that of Malaysian, on in silico basis using 28S rDNA. Continue reading Comparative studies of Indian and Malaysian Thapaocleidus siamensis using molecular marker

