Baby Joseph, Jency George, M.V. Jeevitha
Interdisciplinary Research Centre, Malankara Catholic College, Mariagiri, Kaliakkavilai, Tamil Nadu, India
Key words: Heavy metal, heat shock protein, toxicity, animals, fish and human.
 Abstract
Abstract
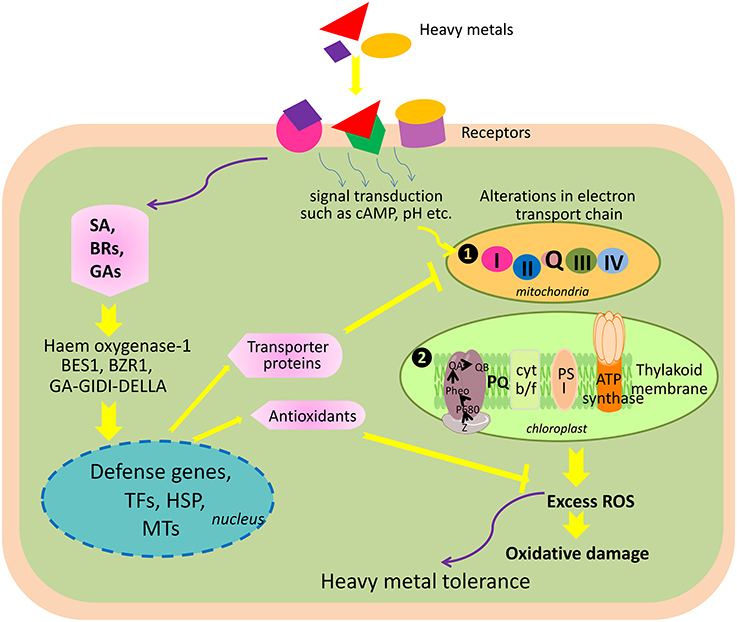
Heavy metals are natural constituents of the earth’s crust, but indiscriminate human activities have drastically altered their geochemical cycles and biochemical balance. Heavy metals such as Iron, copper, Zinc, Nickel, Molybdenum are essential for normal biological functioning. Heavy metals such as Mercury, Lead, and Cadmium are biologically non-essential, but are important metals for industrial applications. Prolonged exposure to heavy metals such as cadmium, copper, lead, nickel, and zinc can cause deleterious health effects in plants, fishes and humans. Higher concentrations of both essential and non-essential metals disturb normal biological functions and which evoke cellular stress responses. Prolonged exposure of heavy metals induces heat shock proteins in plants, animals and fishes. Heat shock proteins are expressed in response to a wide range of biotic and abiotic stressors. Heat shock proteins are a family of highly conserved cellular proteins present in all organisms including fish, plant and humans. This review focus the toxic effects of heavy metals and the significance of heat shock proteins in response to stress in plant, fish and human.
Get the original articles in Source: Volume 2, Number 9, September 2012 – IJB
Published By: International Journal of Biosciences (IJB)
Related Post: Identification of salt tolerant rice genotypes and their genetic diversity analysis using SSR markers
 Abstract
Abstract
