
By: Karima Mohamed El-Absy and Ahmed Mandouh Kamel
Key Words: Soil analysis, Physiological responses, Anatomical responses, Correlation, Teucrium polium, Wadi El-Arbaeen, Wadi El-Obayed
J. Bio. Env. Sci. 15(6), 40-52, December 2019.
Abstract
The objectives of the study were to identify the physiological behavior in soil and plants, to study the anatomical characters as well as the correlations of soil analysis with chemical estimates and amino acids in T. polium plants during spring and autumn seasons in Wadi El-Arbaeen at South Sinai and in Wadi El-Obayed at Marsa Matruh, Egypt. The location, sites and depths in soil properties; locations and seasons in plant chemical compositions and amino acids as well as their interactions were showed significant (P < 0.05 or 0.01) effects.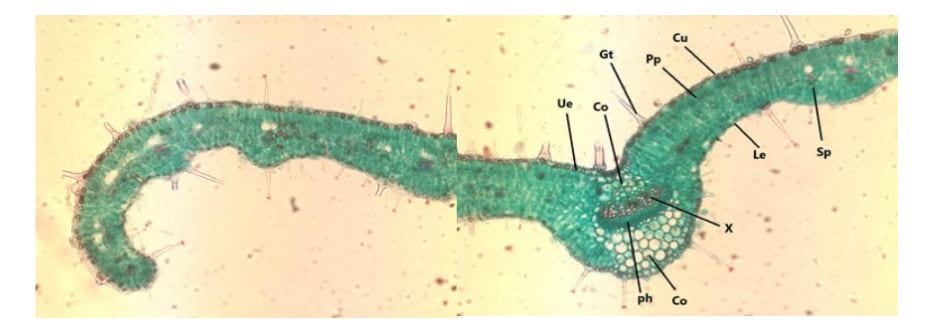

The pH values were higher than 7 in the two depths at the three streams during the two locations. The values of water content, EC, Cl–, Ca2+, Na+ and K+ in soil at the two depths in three streams in Wadi El-Obayed were higher than in Wadi El-Arbaeen. As for plant chemical compositions, succulence ratio, total protein and Mg2+ concentrations in the spring season were higher than in the autumn season under the two studied Wadis. Most concentrations of plant analysis and amino acids concentrations and leaf anatomical characters of T. solium in the Wadi El-Arbaeen were higher than in the Wadi El-Obayed. Proline ranks first in accumulation in T. polium at the spring and autumn seasons, which contributed about 25% and 26% of the total amino acids during Wadi El-Arbaeen and Wadi El-Obayed, respectively. Anatomical characters in T. polium exhibited significant differentiation under Wadi El-Arbaeen and Wadi El-Obayed locations. Positive correlation coefficients were found between water content, EC, pH, Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+ and Cl– in the soil and K+, Na+, Mg2+, total protein; total carbohydrate and succulence ratio in the plants under the two Wadis. Most soil analysis were showed positive correlated with most amino acids during the two locations.
Articles Source : J. Bio. Env. Sci. 15(6), 40-52, December 2019.
Published By : Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES)